
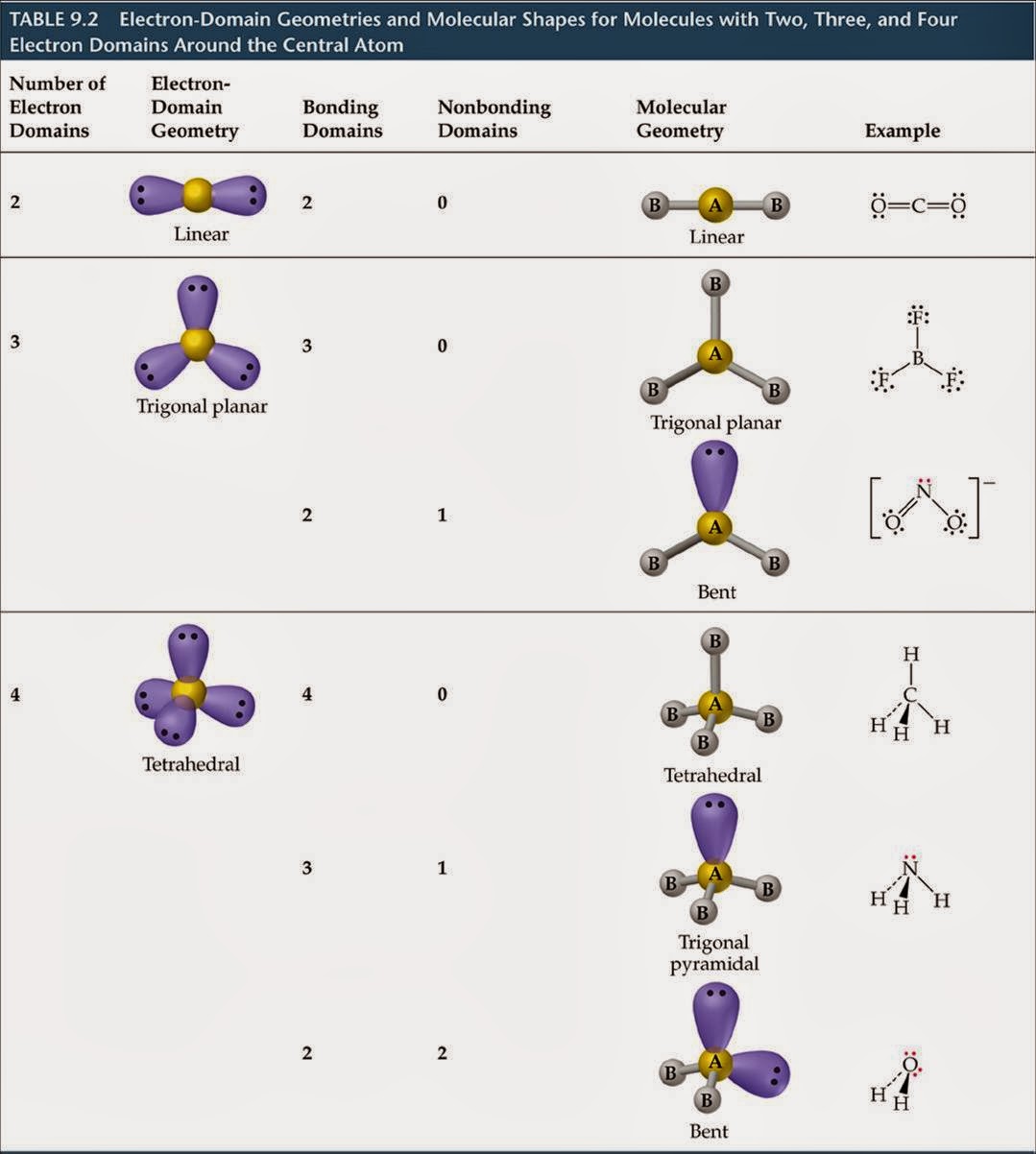
We currently do not have a feature to support diagrams/graphs and will be updating soon. Molecular geometry - The study of the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule is called Molecular geometry. The above discussion explains the electron-pair geometry and molecular geometry of a water molecule. A tetrahedral electron geometry corresponds to sp3 hybridization. There is also lone pair-lone pair repulsion that occurs between the 2 lone pairs of electrons present on the central O atom so due to this reason, the two bond pairs acquire a bent shape. What Is Ch3CH3 + (Methylium cation) Molecular Geometry, Bond Angles Wayne Breslyn 631K. On the other hand, only the 2 bond pairs (2 O-H bonds) are considered in the molecular geometry of H₂O.
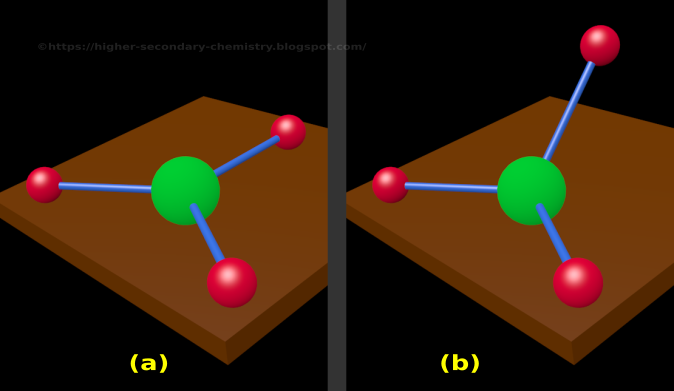
In the electron-pair geometry of H₂O, there are a total of 4 electron groups (2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs of electrons). Also, 2 lone pairs of electrons are present on the central O atom. Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It is a group 14 hydride and the simplest alkane, and is the main component of natural gas. In the structure of a water (H₂O) molecule, it is observed that the central atom is an oxygen (O) atom and it is attached to 2 Hydrogen (H) atoms. Methane (US /men/ or UK /mien/) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4 (one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen). No lone pairs of electrons are considered in the case of molecular geometry. The electron-pair geometry deals with the arrangement of all the electron groups present (considers both bond and lone pairs of electrons) whereas molecular geometry is determined when only bond electron pairs are considered. Ligand substitution reactions have been studied for both structural types and are rapid on the NMR time scale at ambient temperature.There is a difference between electron-pair geometry and the molecular shape of a molecule. When dissolved in chlorinated solvents, the latter compound promotes chlorine atom abstraction, forming tetrahedral (dppe)Fe(Mes)Cl and (dppe)FeCl2. On the other hand, only the 2 bond pairs (2 O-H bonds) are considered in the molecular geometry of HO. A combination of crystallographic and magnetic susceptibility data for (depe)Fe(Mes)2 (depe = 1,2-bis(diethylphosphino)ethane) established a tetrahedral molecular geometry whereas SQUID magnetometry and Mössbauer spectroscopy on samples of (dppe)Fe(Mes)2 (dppe = 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane) indicated a planar molecule. The molecular geometry of CBr4 is Tetrahedral. CBr4 is a nonpolar molecule because of the zero net dipole moment caused by its symmetrical structure. The hybridization of CBr4 is Sp 3 and the bond angle of 109.5°. The hydrogen atoms are as far apart as possible at 109 o bond angle. The carbon has 4 valence electrons and thus needs 4 more electrons from four hydrogen atoms to complete its octet. SiO2 bonds in a tetrahedral pattern where each O atom is shared by two Si atoms.

The molecular geometry of C3H8 is tetrahedral with respect to a carbon atom. Tetrahedral Molecular Geometry Methane: Chime in new window An example of tetrahedral electron pair geometry (E. Determine the molecular geometry and molecular polarity for Question. In contrast, both tetrahedral and square planar coordination has been observed upon complexation of chelating phosphine ligands. The total valence electron is available for drawing the carbon tetrabromide ( CBr4) lewis structure is 32. C3h8o Molecular Geometr圜4H8O, molecular geometry, valence electrons and 3D. Identification of the geometry has been accomplished by a combination of solution and solid-state magnetometry and, in two cases (P = PMe3, PEt2Ph), X-ray diffraction. Treatment of Fe2(Mes)4 (Mes = 2,4,6-Me3C6H2) with monodentate phosphine and phosphite ligands furnished square planar trans-P2Fe(Mes)2 derivatives. The geometric preferences of a family of four coordinate, iron(II) d6 complexes of the general form L2FeX2 have been systematically evaluated.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
